
This global map viewer shows the number of people affected by the COVID-19 pandemic down to the U.S.-county level, and provides data on age and sex groups that can help identify populations most at risk.
February 26, 2019

Two data products and a companion visualization tool released through the NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center operated by CIESIN, provide data on man-made impervious surfaces and urban extents throughout the world, in greater detail than previously available.
February 7, 2018

To what degree do so-called “green” countries depend on the import of goods and services from countries considered more polluting? To help answer this question, CIESIN associate director for Science Applications Alex de Sherbinin and senior research associate Valentina Mara developed a Green Imports Index (GII) that builds on the 2018 Environmental Performance Index, to evaluate whether wealthy countries receive high scores at the expense of rapidly industrializing developing countries.
April 5, 2017

For more than a decade, SEDAC has updated the Natural Resource Protection Indicator and Child Health Indicator data annually for the Millennium Challenge Corporation, a grant-making arm of the U.S. government. This data collection supports the goals of the U.S. Millennium Challenge Corporation by providing data to develop selection criteria for low-income countries’ eligibility for development funding.
May 3, 2016
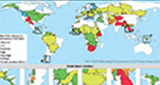
Risks for the world’s Transboundary River Basins are projected to increase in the next 15–30 years, particularly in four hotspot regions: the Middle East, Central Asia, the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna basin, and the Orange and Limpopo basins in Southern Africa. Transboundary river basins cross international borders and are shared by two or more countries, which often makes managing them more challenging. A major report on the status and future threats to the world’s 286 transboundary river basins, funded by the Global Environmental Facility’s Transboundary Waters Assessment Program, has been released by a consortium of institutions led by the UNEP-DHI Center for Water and Environment, including the Earth Institute’s Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN).
March 24, 2016
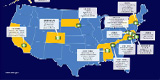
In this blog post for the International Council for Science (ICSU) World Data System (WDS), Alex de Sherbinin, CIESIN associate director for science applications and a member of the WDS Scientific Committee, describes how the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) survey is an important performance metric for the NASA Distributed Active Archive Centers, of which SEDAC is one.
June 11, 2015
May 6, 2015

A new Web-based mapping platform that integrates the Global Population of the World data may help G7+ states manage these resources strategically and sustainably, to accelerate growth and development.
March 24, 2015
March 18, 2015
September 3, 2014
June 2, 2014
April 2, 2014