Gridded Population of the World (GPW), v3
Follow Us: Twitter Follow Us on Facebook YouTube Flickr | Share: Twitter FacebookGPW and GRUMP: A Brief Background, Comparison, and History
Note: The latest version of Gridded Population of the World, GPWv4.11, is available here: https://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/gpw-v4
Gridded Population of the World, Version Three (GPWv3)
This is a gridded, or raster, data product that renders global population data at the scale and extent required to demonstrate the spatial relationship of human populations and the environment across the globe.The purpose of GPW is to provide a spatially disaggregated population layer that is compatible with data sets from social, economic, and Earth science fields.The gridded data set is constructed from national or subnational input units (usually administrative units) of varying resolutions. The native grid cell resolution is 2.5 arc-minutes, or ~5km at the equator, although aggregates at coarser resolutions are also provided. Separate grids are available for population count and density per grid cell.
Population data estimates are provided for 1990, 1995, and 2000, and projected to 2005, 2010, and 2015. The projected grids were produced in collaboration with the United Nations Food and Agriculture Programme (FAO) as Population Count and Density Grid Future Estimates. There is also an extensive map collection that includes population density and sub-national administrative boundary maps (depicting the input units) at country, continental, and global levels. Summary information on the size and number of input unit and sources is available in an Excel spreadsheet.
GPWv3 incorporates a number of improvements to the two prior versions of GPW.The number of input administrative units has increased three-fold since GPWv2 and twenty-fold since GPWv1. The table below provides further points of comparison.
Global Rural-Urban Mapping Project, Version One (GRUMPv1)
This project builds on GPW to construct a common geo-referenced framework of urban and rural areas by combining census data with satellite data. GRUMPv1 actually comprises three data products. First, GRUMPv1 provides a higher resolution gridded population data product at 30 arc-seconds, or ~1km at the equator, for 1990, 1995, and 2000. Second, GRUMPv1’s urban extents data set delineates urban areas based on NOAA’s night-time lights data set and buffered settlement centroids (where night lights are not sufficiently bright). Third, GRUMPv1 provides a points data set of all urban areas with populations of greater than 1,000 persons, which may be downloaded in Excel, CSV, and shapefile formats. As with GPW, there is an extensive map collection depicting the data sets at country, continental, and global levels.
Which Product to Use: GPW or GRUMP
The choice of GPW or GRUMP grids will depend on the application. GRUMP is lightly modeled based on night-time lights, so if the application demands native population data that are rendered in gridded format, then GPW would be preferred. Processing time would also be slightly faster with GPW’s coarser resolution. However, if neither of these factors is a constraint, then it is generally advisable to use GRUMP, which provides a higher- resolution data product that moves populations out of thinly settled large administrative units into settlements. For further information on the methodologies used to construct the data sets, papers on the methods page provide more information on how each data set was constructed.
For more information about GPW, GRUMP, and a comparison to Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Landscan data product, visit the FAQs.
The table below shows how the GPW has developed and expanded over the years and how GRUMP further expands on this work.
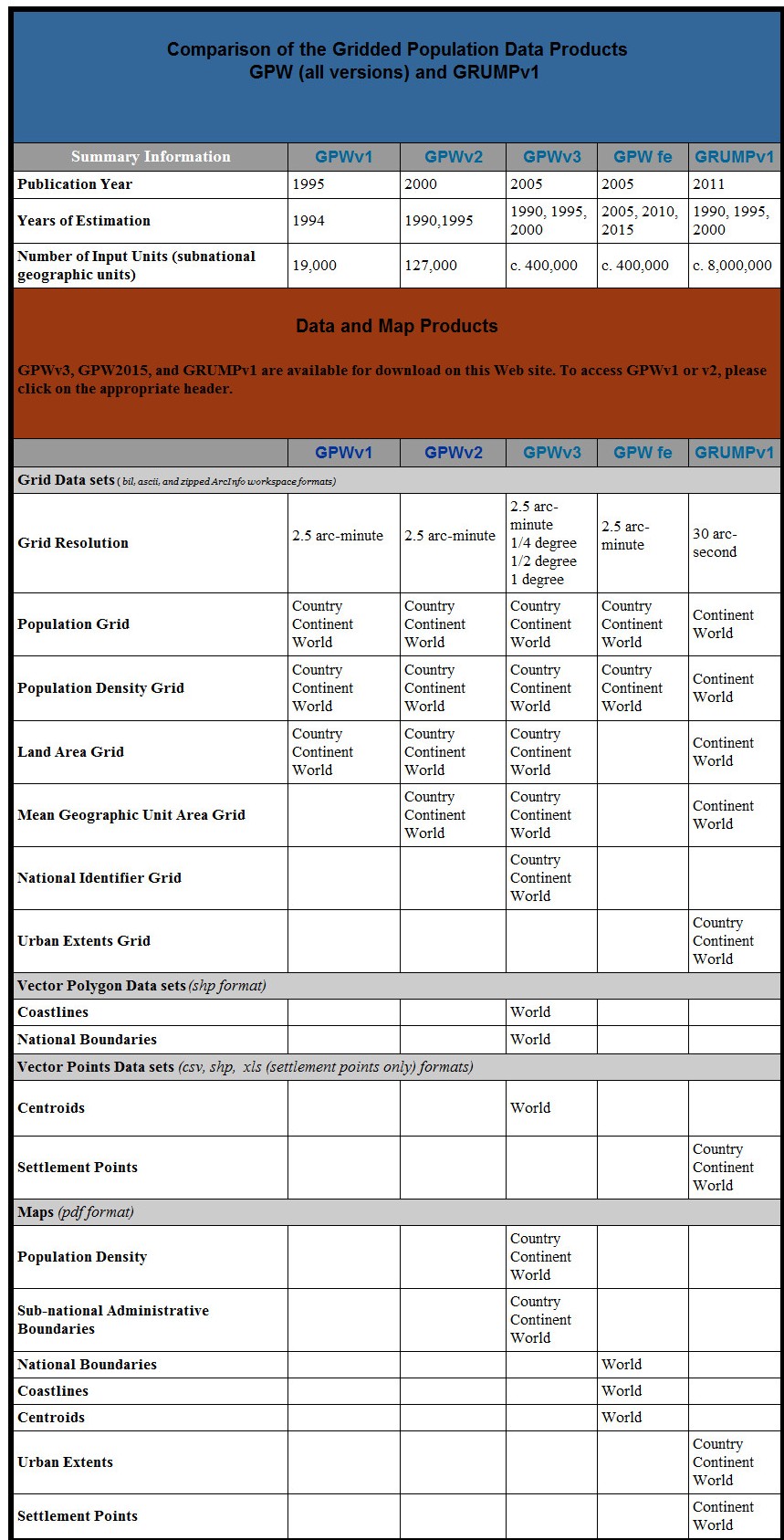
History of the Development of GPW
The initial Gridded Population of the World (GPW) data set, GPWv1, is an outgrowth of a Global Demography Workshop held at CIESIN in 1994. It was produced by Waldo Tobler, Uwe Deichmann, Jan Gottsegen, and Kelley Maloy of the National Center for Geographic Information and Analysis (NCGIA), all at the University of California, Santa Barbara, with partial support from CIESIN under U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Grant NAGW-2901. (This data set was superseded by versions two and three and is therefore no longer available online; however, it may be requested via SEDAC User Services.) Early efforts prior to GPW are described in some detail in by Deichmann in an NCGIA report.
Subsequent to version one, Uwe Deichmann made a number of regional improvements to the underlying data set in collaboration with several other institutions. Revisions for Africa were supported by the United Nations Environment Programme/Global Resource Information Database (UNEP-GRID), Sioux Falls and by the World Resources Institute (WRI); and for Asia by UNEP-GRID, Geneva, the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR), and NCGIA. For Latin America, a comprehensive database was assembled by the Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT). Glenn Hyman of CIAT, Ashbindu Singh of UNEP-GRID, Sioux Falls, and Ron Witt and Hy Dao at UNEP-GRID, Geneva were all partners in these efforts. Some of these databases differed in their approach from GPW in that they included access to roads as a means to reallocate population; it is often referred to as an accessibility model for population distribution. Around the same time, Oakridge National Laboratory began developing a highly modeled population surface known as LandScan.
GPWv2 was produced in 1999−2000 by CIESIN in close collaboration with Uwe Deichmann (presently at the World Bank) via a subcontract with the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI). Funding for GPW v2 was provided by the NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC) under contract NAS5-98162 and by the World Resources Institute (WRI). GPWv2 incorporated the basic improvements to the population inputs that occurred in the development of the regional initiatives. Neither GPWv2 nor prior databases included the 2000 rounds of censuses.
The 2000 round of censuses were formally included in GPW version three, which was produced by CIESIN in partnership with the Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT), from mid−2002 through mid−2004. Around the same time, beginning early 2001, CIESIN and colleagues at the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), the World Bank, and CIAT convened to pursue the possibility of constructing a global database of urban and rural areas that could then be used, not only in and of itself, but also to reallocate population.That effort led to the database now known as the GRUMP suite of data products. Like the accessibility models above, the population grid produced by GRUMPv1 is lightly modeled, using urban areas rather than roads.
GPW v3 includes a major update to the underlying population and spatial data, and in its wake, additional updates have been made, for example, to the Africa accessibility model. Similarly, in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), CIESIN and CIAT have constructed a gridded population projection to 2015.