Gridded Population of the World (GPW), v4
Follow Us: Twitter Follow Us on Facebook YouTube Flickr | Share: Twitter FacebookWhat’s a Grid?
Spatial data are often modeled digitally in one of two ways: as vector objects, such as points, lines and polygons, or as a raster surface, a grid composed of regular pixels or cells each having a specific value. Translation between the vector and raster data models, a process sometimes referred to as "gridding" is possible using a number of conventional methods, though none is without error. Below are figures that show how vector data can be gridded using two different methods: a simple majority rule and proportional allocation.
Figure 1 below depicts the translation of categorical (e.g., soil type or land use) vector data to a raster using a simple majority rule. Each polygon in the image on the left has a number representing a category or ranking. Each pixel in the output raster is assigned the value of the polygon in the input vector data set that covers the greatest area of the pixel. Gridding the data using a simple majority rule results in the raster on the right, where each raster pixel contains the values assigned to it from the corresponding vector polygon.
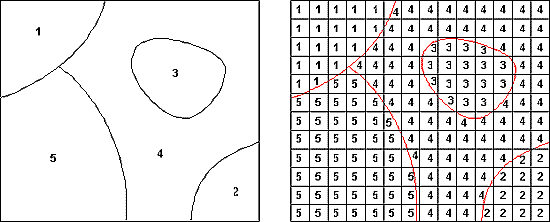
Figure 1 Vector to raster translation: simple majority rule
Proportional allocation is an alternative method for translating vector to raster format that is appropriate for quantitative data (e.g., population). This is the method used to produce GPW. In figure 2, proportional allocation has been used to distribute the value associated with each input vector polygon (left image) equally over all of the raster pixels that are completely within the polygon (right image). Values in the vector image represent the total for each polygon; values in the raster image represent the value assigned to one individual raster pixel. For example, the value 22,000 assigned to the polygon in the upper right part of the vector image is distributed equally to the pixels in the corresponding area of the raster image such that each of those pixels has a value of 98. The raster pixels that intersect multiple input polygons are assigned a value computed based on the proportion of the pixel occupied by each input polygon. Note, in the image on the right, the pixels that cross polygon boundaries have values between those of the cells on either side of the boundary that fall completely within the polygon. One such pixel has been labeled — 14 in the Southeast part of the image.)
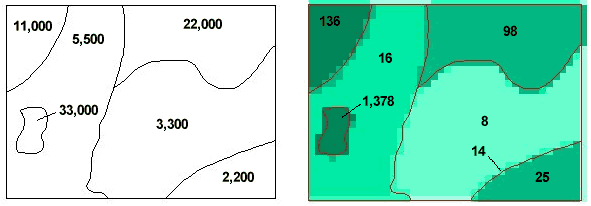
Figure 2 Vector to raster translation: proportional allocation method